To examine the social emotional learning (SEL) critique, I’ve pulled verbatim excerpts (without my synthesis) from websites and news articles that define SEL, describe the genesis of recent critiques, and provide an example of how SEL is being prohibited in schools.
What is SEL?
From the CASEL.org website:
“The Collaborative for Academic, Social, and Emotional Learning (CASEL) has been a leader of the SEL movement since first introducing the term more than two decades ago … We define social and emotional learning (SEL) as an integral part of education and human development. SEL is the process through which all young people and adults acquire and apply the knowledge, skills, and attitudes to develop healthy identities, manage emotions and achieve personal and collective goals, feel and show empathy for others, establish and maintain supportive relationships, and make responsible and caring decisions.
CASEL.org
SEL advances educational equity and excellence through authentic school-family-community partnerships to establish learning environments and experiences that feature trusting and collaborative relationships, rigorous and meaningful curriculum and instruction, and ongoing evaluation. SEL can help address various forms of inequity and empower young people and adults to co-create thriving schools and contribute to safe, healthy, and just communities.”
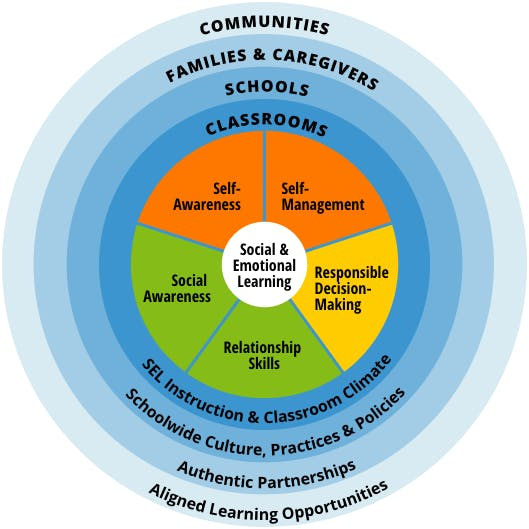
What are the SEL Areas of Competence?
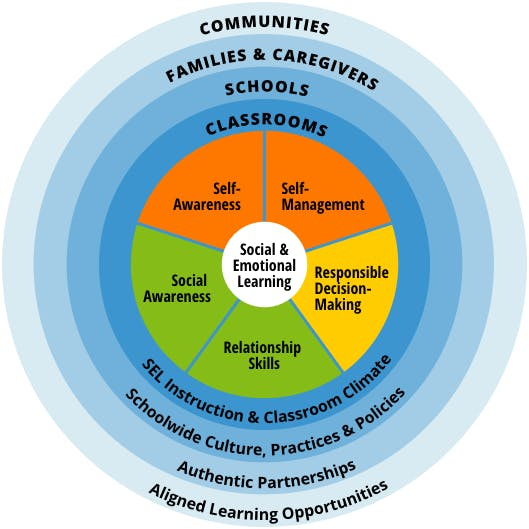
From the CASEL.org website:
“The CASEL 5 addresses five broad and interrelated areas of competence and highlights examples for each: self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, relationship skills, and responsible decision-making. The CASEL 5 can be taught and applied at various developmental stages from childhood to adulthood and across diverse cultural contexts. Many school districts, states, and countries have used the CASEL 5 to establish preschool to high school learning standards and competencies that articulate what students should know and be able to do for academic success, school and civic engagement, health and wellness, and fulfilling careers.”
CASEL.org Framework
What is the critique of SEL?
From NPR.org:
“Although its core concepts have been around nearly as long as public education itself, social-emotional learning is emerging as the latest lightning rod in the battles over what gets taught in schools nationwide Across the country, parents and community members have protested angrily at school board meetings, administrators have distanced themselves from the term and legislators have introduced bills trying to ban it. In the last two years, NPR found evidence of disputes specifically concerning social-emotional learning in at least 25 states.”
“In the last year, in states across the country, parents and community members have increasingly been fighting the teaching of social-emotional learning in schools – largely because social-emotional learning has become linked with another flashpoint in public education: critical race theory, or CRT. Critical race theory, a decades-old legal framework, is the concept that racism goes far beyond the individual: It is systemic and deeply entrenched in our laws, policies and institutions. Nearly 900 school districts experienced anti-CRT protests between September of 2020 and August of last year, according to a report released this year from the Institute for Democracy, Education, and Access at the University of California, Los Angeles.
From NPR.org, “How social-emotional learning became a frontline in the battle against CRT”
How are states prohibiting SEL?
The following provides an example of how Florida is prohibiting SEL:
SEL in instructional materials are considered extraneous, unsolicited strategies prohibited in the specifications for the texts and are not part of the subject-area standards. These include:
From FLDOE.org “Specifications for the 2022-2023 Florida Instructional Materials Adoption K-12 Social Studies”; See section on Prohibition of Critical Race Theory (CRT) and its Applied Principles and Social Emotional Learning; Aspects of CRT Include Culturally Responsive Teaching and Social Justice:
o Identity and identity identification concepts
o Managing emotion
o Developing relation
Featured Image Photo by CASEL.org